|
| |
| The World Factbook |
|
|
Zimbabwe |
|
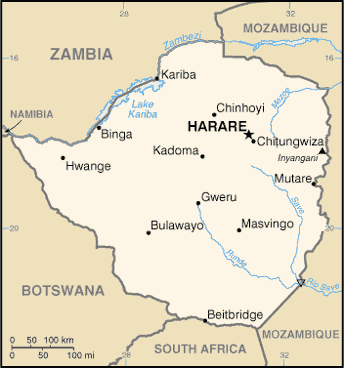
|
|
Background:
|
The UK annexed Southern Rhodesia from the [British] South Africa Company in 1923. A 1961 constitution was formulated that favored whites in power. In 1965 the government unilaterally declared its independence, but the UK did not recognize the act and demanded more complete voting rights for the black African majority in the country (then called Rhodesia). UN sanctions and a guerrilla uprising finally led to free elections in 1979 and independence (as Zimbabwe) in 1980. Robert MUGABE, the nation's first prime minister, has been the country's only ruler (as president since 1987) and has dominated the country's political system since independence. His chaotic land redistribution campaign, which began in 2000, caused an exodus of white farmers, crippled the economy, and ushered in widespread shortages of basic commodities. Ignoring international condemnation, MUGABE rigged the 2002 presidential election to ensure his reelection. The ruling ZANU-PF party used fraud and intimidation to win a two-thirds majority in the March 2005 parliamentary election, allowing it to amend the constitution at will and recreate the Senate, which had been abolished in the late 1980s. In April 2005, Harare embarked on Operation Restore Order, ostensibly an urban rationalization program, which resulted in the destruction of the homes or businesses of 700,000 mostly poor supporters of the opposition. President MUGABE in June 2007 instituted price controls on all basic commodities causing panic buying and leaving store shelves empty for months. General elections held in March 2008 contained irregularities but still amounted to a censure of the ZANU-PF-led government with significant gains in opposition seats in parliament. MDC opposition leader Morgan TSVANGIRAI won the presidential polls, and may have won an out right majority, but official results posted by the Zimbabwe Electoral Committee did not reflect this. In the lead up to a run-off election in late June 2008, considerable violence enacted against opposition party members led to the withdrawal of TSVANGIRAI from the ballot. Extensive evidence of vote tampering and ballot-box stuffing resulted in international condemnation of the process, and calls for the creation of a power-sharing government have been ignored.
|
|
Location:
|
Southern Africa, between South Africa and Zambia
|
|
Geographic coordinates:
|
20 00 S, 30 00 E
|
|
Map references:
|
Africa
|
|
Area:
|
total: 390,580 sq km
land: 386,670 sq km
water: 3,910 sq km
|
|
Area - comparative:
|
slightly larger than Montana
|
|
Land boundaries:
|
total: 3,066 km
border countries: Botswana 813 km, Mozambique 1,231 km, South Africa 225 km, Zambia 797 km
|
|
Coastline:
|
0 km (landlocked)
|
|
Maritime claims:
|
none (landlocked)
|
|
Climate:
|
tropical; moderated by altitude; rainy season (November to March)
|
|
Terrain:
|
mostly high plateau with higher central plateau (high veld); mountains in east
|
|
Elevation extremes:
|
lowest point: junction of the Runde and Save rivers 162 m
highest point: Inyangani 2,592 m
|
|
Natural resources:
|
coal, chromium ore, asbestos, gold, nickel, copper, iron ore, vanadium, lithium, tin, platinum group metals
|
|
Land use:
|
arable land: 8.24%
permanent crops: 0.33%
other: 91.43% (2005)
|
|
Irrigated land:
|
1,740 sq km (2003)
|
|
Total renewable water resources:
|
20 cu km (1987)
|
|
Freshwater withdrawal (domestic/industrial/agricultural):
|
total: 4.21 cu km/yr (14%/7%/79%)
per capita: 324 cu m/yr (2002)
|
|
Natural hazards:
|
recurring droughts; floods and severe storms are rare
|
|
Environment - current issues:
|
deforestation; soil erosion; land degradation; air and water pollution; the black rhinoceros herd - once the largest concentration of the species in the world - has been significantly reduced by poaching; poor mining practices have led to toxic waste and heavy metal pollution
|
|
Environment - international agreements:
|
party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Desertification, Endangered Species, Law of the Sea, Ozone Layer Protection
signed, but not ratified: none of the selected agreements
|
|
Geography - note:
|
landlocked; the Zambezi forms a natural riverine boundary with Zambia; in full flood (February-April) the massive Victoria Falls on the river forms the world's largest curtain of falling water
|
|
Population:
|
11,350,111
note: estimates for this country explicitly take into account the effects of excess mortality due to AIDS; this can result in lower life expectancy, higher infant mortality, higher death rates, lower population growth rates, and changes in the distribution of population by age and sex than would otherwise be expected (July 2008 est.)
|
|
Age structure:
|
0-14 years: 43.9% (male 2,514,135/female 2,465,715)
15-64 years: 52.3% (male 2,671,164/female 3,260,457)
65 years and over: 3.9% (male 194,854/female 243,786) (2008 est.)
|
|
Median age:
|
total: 17.6 years
male: 16.4 years
female: 18.8 years (2008 est.)
|
|
Population growth rate:
|
-0.787% (2008 est.)
|
|
Birth rate:
|
31.62 births/1,000 population (2008 est.)
|
|
Death rate:
|
17.29 deaths/1,000 population (2008 est.)
|
|
Net migration rate:
|
NA
note: there is an increasing flow of Zimbabweans into South Africa and Botswana in search of better economic opportunities (2008 est.)
|
|
Sex ratio:
|
at birth: 1.03 male(s)/female
under 15 years: 1.02 male(s)/female
15-64 years: 0.82 male(s)/female
65 years and over: 0.8 male(s)/female
total population: 0.885 male(s)/female (2008 est.)
|
|
Infant mortality rate:
|
total: 33.86 deaths/1,000 live births
male: 36.5 deaths/1,000 live births
female: 31.14 deaths/1,000 live births (2008 est.)
|
|
Life expectancy at birth:
|
total population: 44.28 years
male: 45.08 years
female: 43.46 years (2008 est.)
|
|
Total fertility rate:
|
3.72 children born/woman (2008 est.)
|
|
HIV/AIDS - adult prevalence rate:
|
24.6% (2001 est.)
|
|
HIV/AIDS - people living with HIV/AIDS:
|
1.8 million (2001 est.)
|
|
HIV/AIDS - deaths:
|
170,000 (2003 est.)
|
|
Major infectious diseases:
|
degree of risk: high
food or waterborne diseases: bacterial and protozoal diarrhea, hepatitis A, and typhoid fever
vectorborne disease: malaria
water contact disease: schistosomiasis
animal contact disease: rabies (2008)
|
|
Nationality:
|
noun: Zimbabwean(s)
adjective: Zimbabwean
|
|
Ethnic groups:
|
African 98% (Shona 82%, Ndebele 14%, other 2%), mixed and Asian 1%, white less than 1%
|
|
Religions:
|
syncretic (part Christian, part indigenous beliefs) 50%, Christian 25%, indigenous beliefs 24%, Muslim and other 1%
|
|
Languages:
|
English (official), Shona, Sindebele (the language of the Ndebele, sometimes called Ndebele), numerous but minor tribal dialects
|
|
Literacy:
|
definition: age 15 and over can read and write English
total population: 90.7%
male: 94.2%
female: 87.2% (2003 est.)
|
|
School life expectancy (primary to tertiary education):
|
total: 9 years
male: 9 years
female: 9 years (2003)
|
|
Education expenditures:
|
4.6% (2000)
|
|
Country name:
|
conventional long form: Republic of Zimbabwe
conventional short form: Zimbabwe
former: Southern Rhodesia, Rhodesia
|
|
Government type:
|
parliamentary democracy
|
|
Capital:
|
name: Harare
geographic coordinates: 17 50 S, 31 03 E
time difference: UTC+2 (7 hours ahead of Washington, DC during Standard Time)
|
|
Administrative divisions:
|
8 provinces and 2 cities* with provincial status; Bulawayo*, Harare*, Manicaland, Mashonaland Central, Mashonaland East, Mashonaland West, Masvingo, Matabeleland North, Matabeleland South, Midlands
|
|
Independence:
|
18 April 1980 (from UK)
|
|
National holiday:
|
Independence Day, 18 April (1980)
|
|
Constitution:
|
21 December 1979
|
|
Legal system:
|
mixture of Roman-Dutch and English common law; has not accepted compulsory ICJ jurisdiction
|
|
Suffrage:
|
18 years of age; universal
|
|
Executive branch:
|
chief of state: Executive President Robert Gabriel MUGABE (since 31 December 1987); Vice President Joseph MSIKA (since December 1999) and Vice President Joyce MUJURU (since 6 December 2004); note - the president is both the chief of state and head of government
head of government: Executive President Robert Gabriel MUGABE (since 31 December 1987); Vice President Joseph MSIKA (since December 1999) and Vice President Joyce MUJURU (since 6 December 2004)
cabinet: Cabinet appointed by the president; responsible to the House of Assembly
elections: presidential candidates nominated with a nomination paper signed by at least 10 registered voters (at least one from each province) and elected by popular vote for a five-year term (no term limits); elections last held 28 March 2008 followed by a run-off on 27 June 2008 (next to be held in 2013); co-vice presidents appointed by the president
election results: Robert Gabriel MUGABE reelected president; percent of vote - Robert Gabriel MUGABE 85.5%, Morgan TSVANGIRAI 9.3%, other 5.2%; note - first round voting results - Morgan TSVANGIRAI 47.9%, Robert Gabriel MUGABE 43.2%, Simba MAKONI 8.3%, other 0.6%; first-round round polls were deemed to be flawed suppressing TSVANGIRAI's results; the 27 June 2008 run-off between MUGABE and TSVANGIRAI were severely flawed and internationally condemned
|
|
Legislative branch:
|
bicameral Parliament consists of a Senate (93 seats - 60 elected by popular vote for a five-year term, 10 provincial governors nominated by the president, 16 traditional chiefs elected by the Council of Chiefs, 2 held by the president and deputy president of the Council of Chiefs, and 5 appointed by the president) and a House of Assembly (210 seats - all elected by popular vote for five-year terms)
elections: last held 28 March 2008 (next to be held in 2013)
election results: Senate - percent of vote by party - MDC 51.6%, ZANU-PF 45.8%, other 2.6%; seats by party - MDC 30, ZANU-PF 30; House of Assembly - percent of vote by party - MDC 51.3%, ZANU-PF 45.8%, other 2.9%; seats by party - MDC 109, ZANU-PF 97, other 4
|
|
Judicial branch:
|
Supreme Court; High Court
|
|
Political parties and leaders:
|
African National Party or ANP [Egypt DZINEMUNHENZVA]; Movement for Democratic Change or MDC [Morgan TSVANGIRAI, anti-Senate faction; Arthur MUTAMBARA, pro-Senate faction]; Peace Action is Freedom for All or PAFA; United Parties [Abel MUZOREWA]; United People's Party or UPP [Daniel SHUMBA]; Zimbabwe African National Union-Ndonga or ZANU-Ndonga [Wilson KUMBULA]; Zimbabwe African National Union-Patriotic Front or ZANU-PF [Robert Gabriel MUGABE]; Zimbabwe African Peoples Union or ZAPU [Agrippa MADLELA]; Zimbabwe Youth in Alliance or ZIYA
|
|
Political pressure groups and leaders:
|
Crisis in Zimbabwe Coalition [Xolani ZITHA]; National Constitutional Assembly or NCA [Lovemore MADHUKU]; Women of Zimbabwe Arise or WOZA [Jenny WILLIAMS]; Zimbabwe Congress of Trade Unions or ZCTU [Wellington CHIBEBE]
|
|
International organization participation:
|
ACP, AfDB, AU, COMESA, FAO, G-15, G-77, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICCt (signatory), ICRM, IDA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, ILO, IMF, IMO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, ITUC, MIGA, NAM, OPCW, PCA, SADC, UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNIDO, UNMIS, UNOCI, UNWTO, UPU, WCL, WCO, WFTU, WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO
|
|
Diplomatic representation in the US:
|
chief of mission: Ambassador Marina Annette VALERE
chancery: 1608 New Hampshire Avenue NW, Washington, DC 20009
telephone: [1] (202) 332-7100
FAX: [1] (202) 483-9326
|
|
Diplomatic representation from the US:
|
chief of mission: Ambassador James D. MCGEE
embassy: 172 Herbert Chitepo Avenue, Harare
mailing address: P. O. Box 3340, Harare
telephone: [263] (4) 250-593 and 250-594
FAX: [263] (4) 796-488
|
|
Flag description:
|
seven equal horizontal bands of green, yellow, red, black, red, yellow, and green with a white isosceles triangle edged in black with its base on the hoist side; a yellow Zimbabwe bird representing the long history of the country is superimposed on a red five-pointed star in the center of the triangle, which symbolizes peace; green symbolizes agriculture, yellow - mineral wealth, red - blood shed to achieve independence, and black stands for the native people
|
|
Economy - overview:
|
The government of Zimbabwe faces a wide variety of difficult economic problems as it struggles with an unsustainable fiscal deficit, an overvalued official exchange rate, hyperinflation, and bare store shelves. Its 1998-2002 involvement in the war in the Democratic Republic of the Congo drained hundreds of millions of dollars from the economy. The government's land reform program, characterized by chaos and violence, has badly damaged the commercial farming sector, the traditional source of exports and foreign exchange and the provider of 400,000 jobs, turning Zimbabwe into a net importer of food products. The EU and the US provide food aid on humanitarian grounds. Badly needed support from the IMF has been suspended because of the government's arrears on past loans and the government's unwillingness to enact reforms that would stabilize the economy. The Reserve Bank of Zimbabwe routinely prints money to fund the budget deficit, causing the official annual inflation rate to rise from 32% in 1998, to 133% in 2004, 585% in 2005, passed 1000% in 2006, and 26000% in November 2007. Private sector estimates of inflation in 2007 are well above 100,000%. Meanwhile, the official exchange rate fell from approximately 1 (revalued) Zimbabwean dollar per US dollar in 2003 to 30,000 per US dollar in 2007.
|
|
GDP (purchasing power parity):
|
$2.211 billion (2007 est.)
|
|
GDP (official exchange rate):
|
$1.726 billion
note: hyperinflation and the plunging value of the Zimbabwean dollar makes Zimbabwe's GDP at the official exchange rate a highly inaccurate statistic (2007 est.)
|
|
GDP - real growth rate:
|
-6.1% (2007 est.)
|
|
GDP - per capita (PPP):
|
$200 (2007 est.)
|
|
GDP - composition by sector:
|
agriculture: 18.1%
industry: 22.6%
services: 59.3% (2007 est.)
|
|
Labor force:
|
4.032 million (2007 est.)
|
|
Labor force - by occupation:
|
agriculture: 66%
industry: 10%
services: 24% (1996)
|
|
Unemployment rate:
|
80% (2005 est.)
|
|
Population below poverty line:
|
68% (2004)
|
|
Household income or consumption by percentage share:
|
lowest 10%: 2%
highest 10%: 40.4% (1995)
|
|
Distribution of family income - Gini index:
|
50.1 (2006)
|
|
Inflation rate (consumer prices):
|
10,453% official data; private sector estimates are much higher (2007 est.)
|
|
Investment (gross fixed):
|
16.9% of GDP (2007 est.)
|
|
Budget:
|
revenues: $2.442 billion
expenditures: $3.017 billion (2007 est.)
|
|
Public debt:
|
211.9% of GDP (2007 est.)
|
|
Agriculture - products:
|
corn, cotton, tobacco, wheat, coffee, sugarcane, peanuts; sheep, goats, pigs
|
|
Industries:
|
mining (coal, gold, platinum, copper, nickel, tin, clay, numerous metallic and nonmetallic ores), steel; wood products, cement, chemicals, fertilizer, clothing and footwear, foodstuffs, beverages
|
|
Industrial production growth rate:
|
0.2% (2007 est.)
|
|
Electricity - production:
|
9.95 billion kWh (2005)
|
|
Electricity - production by source:
|
fossil fuel: 47%
hydro: 53%
nuclear: 0%
other: 0% (2001)
|
|
Electricity - consumption:
|
12.27 billion kWh (2005)
|
|
Electricity - exports:
|
0 kWh (2005)
|
|
Electricity - imports:
|
3.013 billion kWh (2005)
|
|
Oil - production:
|
0 bbl/day (2005 est.)
|
|
Oil - consumption:
|
16,000 bbl/day (2005 est.)
|
|
Oil - exports:
|
0 bbl/day (2004 est.)
|
|
Oil - imports:
|
13,370 bbl/day (2004 est.)
|
|
Oil - proved reserves:
|
0 bbl (1 January 2006 est.)
|
|
Natural gas - production:
|
0 cu m (2005 est.)
|
|
Natural gas - consumption:
|
0 cu m (2005 est.)
|
|
Natural gas - exports:
|
0 cu m (2005 est.)
|
|
Natural gas - imports:
|
0 cu m (2005)
|
|
Natural gas - proved reserves:
|
0 cu m (1 January 2006 est.)
|
|
Current account balance:
|
-$116 million (2005 est.)
|
|
Exports:
|
$1.52 billion f.o.b. (2007 est.)
|
|
Exports - commodities:
|
platinum, cotton, tobacco, gold, ferroalloys, textiles/clothing
|
|
Exports - partners:
|
South Africa 16.4%, Democratic Republic of the Congo 11.6%, Japan 11.5%, Botswana 10.4%, Netherlands 7.4%, China 6.9%, Italy 5.8% (2006)
|
|
Imports:
|
$2.183 billion f.o.b. (2007 est.)
|
|
Imports - commodities:
|
machinery and transport equipment, other manufactures, chemicals, fuels
|
|
Imports - partners:
|
South Africa 39.1%, Zambia 28.4%, China 5.5% (2006)
|
|
Economic aid - recipient:
|
$367.7 million (2005 est.)
|
|
Reserves of foreign exchange and gold:
|
$120 million (31 December 2007 est.)
|
|
Debt - external:
|
$5.155 billion (31 December 2007 est.)
|
|
Stock of direct foreign investment - at home:
|
$NA
|
|
Stock of direct foreign investment - abroad:
|
$NA
|
|
Market value of publicly traded shares:
|
$26.56 billion (2006)
|
|
Currency (code):
|
Zimbabwean dollar (ZWD)
|
|
Currency code:
|
ZWD
|
|
Exchange rates:
|
Zimbabwean dollars per US dollar - 30,000 (2007), 162.07 (2006), 77.965 (2005), 5.729 (2004), 0.824 (2003)
note: these are official exchange rates; non-official rates vary significantly
|
|
Fiscal year:
|
calendar year
|
|
Telephones - main lines in use:
|
331,700 (2006)
|
|
Telephones - mobile cellular:
|
1.226 million (2007)
|
|
Telephone system:
|
general assessment: system was once one of the best in Africa, but now suffers from poor maintenance; more than 100,000 outstanding requests for connection despite an equally large number of installed but unused main lines
domestic: consists of microwave radio relay links, open-wire lines, radiotelephone communication stations, fixed wireless local loop installations, and a substantial mobile-cellular network; Internet connection is available in Harare and planned for all major towns and for some of the smaller ones
international: country code - 263; satellite earth stations - 2 Intelsat; 2 international digital gateway exchanges (in Harare and Gweru)
|
|
Radio broadcast stations:
|
AM 7, FM 20 (plus 17 repeater stations), shortwave 1 (1998)
|
|
Radios:
|
1.14 million (1997)
|
|
Television broadcast stations:
|
16 (1997)
|
|
Televisions:
|
370,000 (1997)
|
|
Internet country code:
|
.zw
|
|
Internet hosts:
|
15,507 (2007)
|
|
Internet Service Providers (ISPs):
|
6 (2000)
|
|
Internet users:
|
1.22 million (2006)
|
|
Airports:
|
341 (2007)
|
|
Airports - with paved runways:
|
total: 19
over 3,047 m: 3
2,438 to 3,047 m: 2
1,524 to 2,437 m: 4
914 to 1,523 m: 10 (2007)
|
|
Airports - with unpaved runways:
|
total: 322
1,524 to 2,437 m: 4
914 to 1,523 m: 152
under 914 m: 166 (2007)
|
|
Pipelines:
|
refined products 270 km (2007)
|
|
Railways:
|
total: 3,077 km
narrow gauge: 3,077 km 1.067-m gauge (313 km electrified) (2006)
|
|
Roadways:
|
total: 97,440 km
paved: 18,514 km
unpaved: 78,926 km (2002)
|
|
Waterways:
|
on Lake Kariba (2005)
|
|
Ports and terminals:
|
Binga, Kariba
|
|
Military branches:
|
Zimbabwe Defense Forces (ZDF): Zimbabwe National Army, Air Force of Zimbabwe (AFZ), Zimbabwe Republic Police (2005)
|
|
Military service age and obligation:
|
18-24 years of age for compulsory military service; women are eligible to serve (2007)
|
|
Manpower available for military service:
|
males age 16-49: 3,264,258
females age 16-49: 3,048,049 (2008 est.)
|
|
Manpower fit for military service:
|
males age 16-49: 1,643,036
females age 16-49: 1,404,663 (2008 est.)
|
|
Military expenditures:
|
3.8% (2006)
|
| Transnational Issues |
Zimbabwe |
|
Disputes - international:
|
Botswana built electric fences and South Africa has placed military along the border to stem the flow of thousands of Zimbabweans fleeing to find work and escape political persecution; Namibia has supported, and in 2004 Zimbabwe dropped objections to, plans between Botswana and Zambia to build a bridge over the Zambezi River, thereby de facto recognizing a short, but not clearly delimited, Botswana-Zambia boundary in the river
|
|
Refugees and internally displaced persons:
|
refugees (country of origin): 2,500 (Democratic Republic of Congo)
IDPs: 569,685 (MUGABE-led political violence, human rights violations, land reform, and economic collapse) (2007)
|
|
Trafficking in persons:
|
current situation: Zimbabwe is a source, transit, and destination country for men, women, and children trafficked for the purposes of forced labor and sexual exploitation; large scale migration of Zimbabweans to surrounding countries - as they flee a progressively more desperate situation at home - has increased; rural Zimbabwean men, women, and children are trafficked internally to farms for agricultural labor and domestic servitude and to cities for domestic labor and commercial sexual exploitation; young men and boys are trafficked to South Africa for farm work, often laboring for months in South Africa without pay before "employers" have them arrested and deported as illegal immigrants; young women and girls are lured abroad with false employment offers that result in involuntary domestic servitude or commercial sexual exploitation; men, women, and children from neighboring states are trafficked through Zimbabwe en route to South Africa
tier rating: Tier 2 Watch List - Zimbabwe is on the Tier 2 Watch List for its failure to provide evidence of increasing efforts to combat severe forms of human trafficking, and because the absolute number of victims of severe forms of trafficking is significantly increasing; the trafficking situation in the country is worsening as more of the population is made vulnerable by declining socio-economic conditions (2008)
|
|
Illicit drugs:
|
transit point for cannabis and South Asian heroin, mandrax, and methamphetamines en route to South Africa
|
|
This page was last updated on 4 September, 2008
|
| | Source : The World Factbook |
| |
|


